
| Home |
| The WEB-Method |
| Examples |
| Publications |
| Contact |
Incompressible Flow
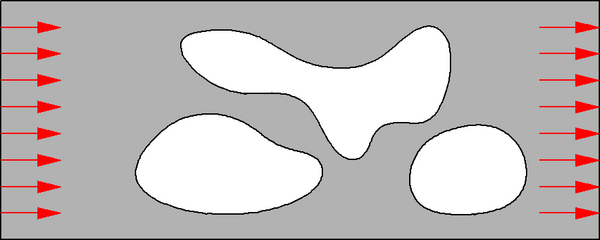
An incompressible fluid passes through a channel with three obstacles (flow speed v=3).
The velocity distribution can be computed by solving the boundary value problem
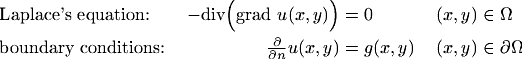
for the potential u(x,y).
At the left end of the channel g=-3, and g=3 at the right end. These natural boundary conditions do not enter explicitly in the variational formulation. Hence, web-splines without weighting can be used for the finite element approximation.
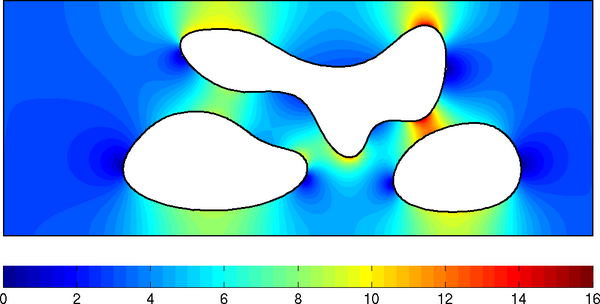
The velocity is visualized in the following Figure.
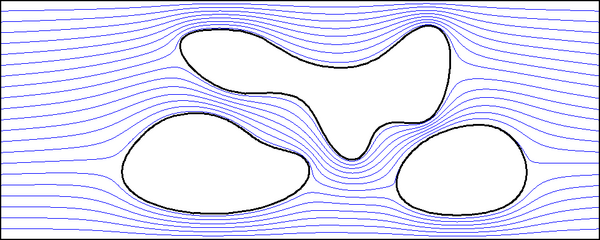
The next Figure shows the streamlines, along which the potential is constant.
Below, the classification of the tensor product B-splines is illustrated. The majority of B-splines (marked blue) does not have to be modified. The percentage of B-splines, coupled with outer B-splines (marked red) tends to zero as the grid is refined.
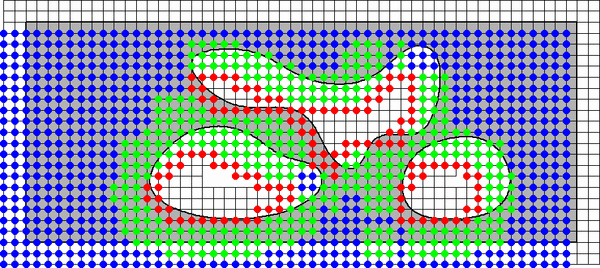
As a consequence of the regular grid structure, the finite element solution can be computed very efficiently.
Literature
K. Höllig, U. Reif, J. Wipper: B-Spline approximation of Neumann problems. Mathematisches Institut A, University of Stuttgart, Preprint 2001-2.See Publications for a complete list of WEB-publications.
Author: Joachim Wipper ; Last modification: 2006/08/31 09:36:55 UTC.
| [Home] [The WEB-Method] [Examples] [Publications] [Contact] |